What is co-insurance?
Despite the prevalence of co-insurance clauses, many people don’t understand what they are or what they’re for.
A co-insurance clause requires policyholders to insure their property to an appropriate value, typically 80%, 90% or 100%, of the true replacement value of that property. It is required by commercial insurance policies (and some personal insurance policies, too).
If you choose a lesser percentage than what is required, you become a ‘co-insurer’ and agree to share covering the costs of any losses with the insurer.
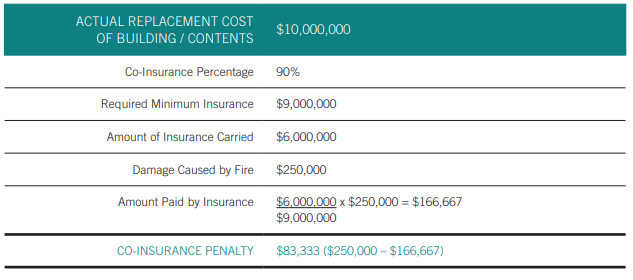
Co-insurance is best illustrated by example:
The co-insurance penalty is the amount paid because the co-insurance percentage was not met (the property was insured for $6,000,000 instead of the required minimum of $9,000,000).
This example puts in dollar terms the co-insurance concept which could be described as:
Co-insurance does not apply to a total loss. In the above example, if there was a total loss, the maximum amount payable would be $6,000,000 which is the amount of insurance carried.
When insuring buildings, remember it is the actual cost of physical re-construction (excluding land value) that needs to be insured. This is the replacement cost or rebuilding cost. This includes the cost of construction materials, labour and replacing property like appliances, equipment, furnishings, finishes and more.
If you have any questions about your co-insurance requirements or claims, please don’t hesitate to contact our team.